Appx 7B - Intra-oral examination. Systematic methods of caries detection.
 Assessing And Documenting Caries Risk
Assessing And Documenting Caries Risk
The CRA may draw upon relevant historical data of the.
Caries risk assessment. Appx 8C - Soft tissue examination. The checklist is divided into 2 main sections. Test that takes into consideration all these factors and can accurately predict an individuals susceptibility to caries.
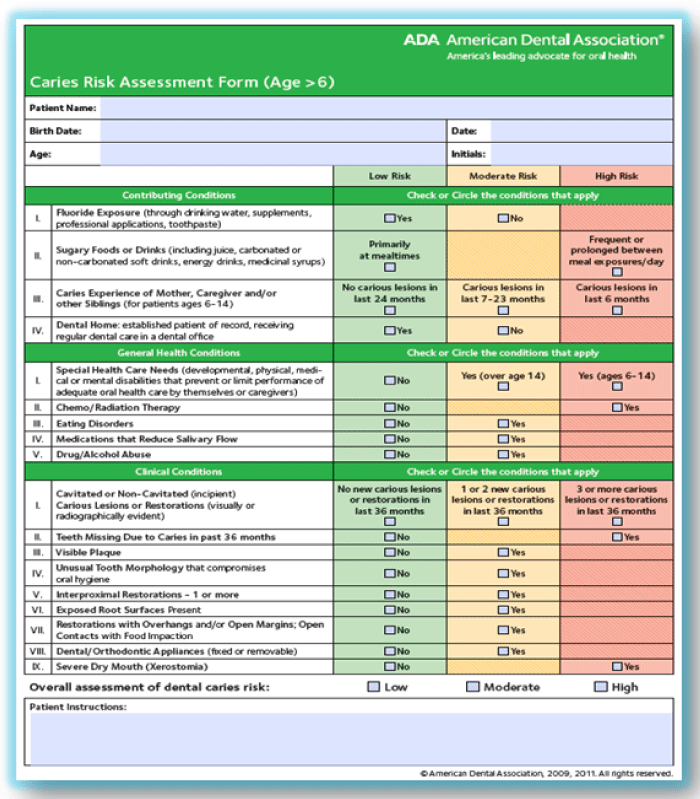
Low Risk Moderate Risk High Risk Contributing Conditions Check or Circle the conditions that apply I. Whether invasive therapy or a more conservative noninvasive approach. Caries-risk assessment is the determination of the likelihood of the increased incidence of caries ie the number of new cavitated or incipient lesions during a certain time period 9 or the likelihood that there will be a change in the size or activity of lesions already present.
Appx 9C - Periodontal screening for under 18. Risk assessment categorization of low moderate or high is based on the preponderance of factors for the individual. Appx 7A - Extra-oral examination.
Caries risk assessment A CRA is simply a way to formalize and expand upon the patients caries balanceimbalance in the most predicable fashion to diagnose current caries e55 Young Featherstone disease to help predict future disease and to determine what factors are out of balance so evidence-based clinical decisions can be made 8 12. The formerly practiced paradigm of drill and fill that is drilling out pits and fissures or surgically removing. Using the Caries Risk Assessment form they will evaluate the bacteria in your mouth diet and the condition of your mouth and teeth.
Fluoride Exposure through drinking water supplements professional applications toothpaste Yes No II. Therefore caries risk assessment may be useful in the clinical management of caries by helping dental professionals do the following. Dental providers should be skilled in assessing an individual patients risk for dental cari.
Appx 5 - Caries risk assessment guide. Of patients with reduced caries risk status After pilot testing train providers and calibrate how low moderate and high risk patients are defined and addressed. Evaluate the degree of the patients risk of developing caries to determine the intensity of the treatment for example a 226 parts per million sodium fluoride NaF rinse versus a 5000 ppm NaF brush-on gel and frequency of recall appointments or treatments.
Appx 9B - Referral policy. Caries-risk Assessment forms were formulated that can be used by dentists to assess caries risk status for 05-year-old and 6-year-old children. Caries-risk assessment Int Dent J.
Low Risk Moderate Risk High Risk Contributing Conditions Check or Circle the conditions that apply I. The risk of dental caries can be evaluated by analysing and integrating several causative factors. Fluoride Exposure through drinking water supplements professional applications toothpaste Yes No II.
The heterogeneity of populations models outcome criteria measures and reporting hampe. It is important to recognize that the scientific evidence. Appx 8A - Oral cancer.
High rates of primary and secondary caries in at-risk populations result in significant lifetime costs. The caries risk assessment forms are not intended to include all possible risk factors. There are several caries risk assessment CRA tools in use today including tools from the American Dental Association ADA and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry AAPD tools based on the Caries Management by Risk Assessment CAMBRA philosophy and software-based prediction tools such as Cariogram and PreViser.
Dental Provider Workflow Patient seated in exam room RDHDA begins clinical assessmentexam RDHDA uses CRA to guide conversation. Sugary Foods or Drinks including juice carbonated or. Sugary Foods or Drinks including juice carbonated or.
How Does the Caries Risk Assessment and Management Work. Appx 9A - Basic periodontal examination. These include caries experience initial caries lesions.
Risk factorsindicators and protective factors. Multivariate models and baseline caries prevalence performed better in pre-school children than in schoolchildrenadolescents. Caries Risk Assessment Form Age 6 Patient Name.
Caries Risk Assessment Form Age 0-6 Patient Name. Appx 8B - Soft tissue lesion monitoring. Authors E Reich 1.
Caries risk assessment Caries remains the most common chronic disease affecting both children and adults in the United States. Key Points Dental caries is defined as a biofilm-mediated sugar-driven multifactorial dynamic disease that results in the. The risk factors selected are intended to provide patient with information that may help them lower the caries risk over time while also provid-ing a form that can be integrated into a busy practice setting.
Caries risk assessment should form the basis of a risk-based approach to patient treatment and recall with repeat assessments indicating if the childs risk status is changing over time. In addition several state Medicaid programs are developing their. The shaded part contains the risk factorsindicators that the Guideline Development Group considered most.
Draws out patient information on risk. Baseline caries prevalence was the most accurate single predictor in all age groups. Caries-risk assessment models currently involve a combina-tion of factors including diet fluoride exposure a susceptible host and microflora that interplay with a variety of social cultural and behavioral factors3-6 Caries risk assessment is the determination of the likelihood of the incidence of caries.
An objective detection method to complement the traditional visual assessment is used by the clinician for arriving at clinical decisions on the management of the carious lesion. Your dental hygienist is the most likely person to assess your caries risk factors as the main focus of their job is prevention. However clinical judgment may justify the use of one factor eg frequent exposure to cariogenic snacks 1 interproximal lesions and low salivary.
Appx 6 - Decision support grid.







/mother-helping-toddler-daughter-cutting-breakfast-waffles-1011589256-5c4dc951c9e77c0001380382.jpg)